Error processing SSI file
Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update
2008-2009 Influenza Season Week 6 ending February 14, 2009
(All data are preliminary and may change as more reports are received.)Synopsis:
During week 6 (February 8-14, 2009), influenza activity continued to increase in the United States.
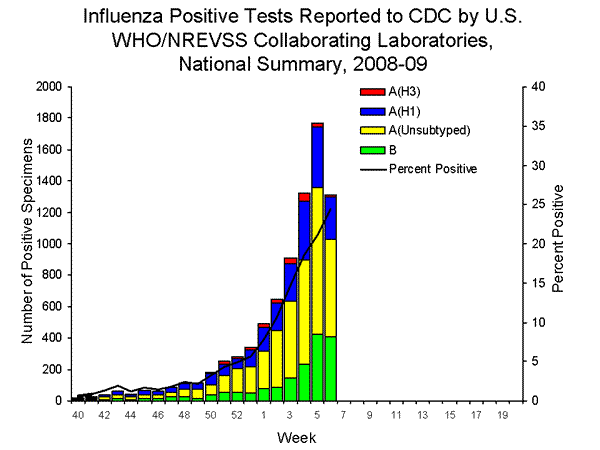
- One thousand three hundred thirteen (24.4%) specimens tested by U.S. World Health Organization (WHO) and National Respiratory and Enteric Virus Surveillance System (NREVSS) collaborating laboratories and reported to CDC/Influenza Division were positive for influenza.
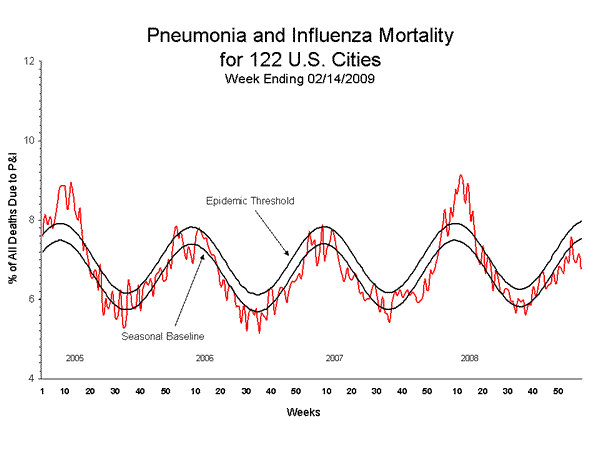
- The proportion of deaths attributed to pneumonia and influenza (P&I) was below the epidemic threshold.
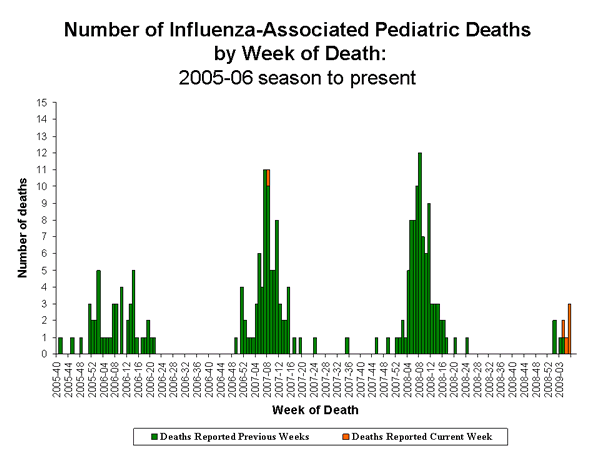
- Six influenza-associated pediatric deaths were reported.
- The proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) was above the national baseline. ILI increased in seven of the nine regions compared to the previous week, and the East North Central, East South Central, Mid-Atlantic, Mountain, New England, South Atlantic, West North Central, and West South Central regions reported ILI above their region-specific baselines.
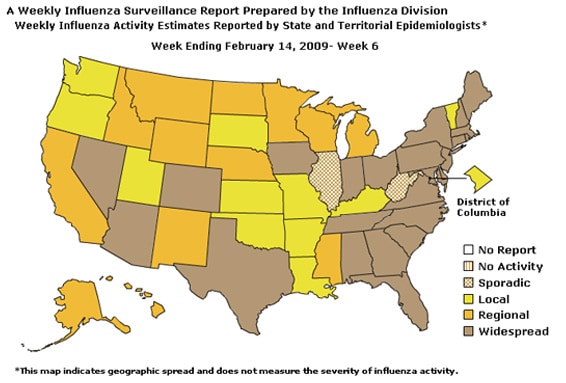
- Twenty-four states reported widespread influenza activity, 13 states reported regional activity; the District of Columbia and 11 states reported local influenza activity; and Puerto Rico and two states reported sporadic influenza activity.
Region |
Data for current week | Data cumulative for the season | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Out-patient ILI* | % positive for flu?/strong> | Number of jurisdictions reporting regional or widespread activity?/strong> | A (H1) | A (H3) | A Unsub-typed | B | Pediatric Deaths | |
| Nation | Elevated | 24.4 % | 37 of 51 | 2,120 | 249 | 4,073 | 1,678 | 9 |
| New England | Elevated | 25.1 % | 5 of 6 | 175 | 19 | 338 | 120 | 0 |
| Mid-Atlantic | Elevated | 17.2 % | 3 of 3 | 195 | 19 | 319 | 134 | 2 |
| East North Central | Elevated | 39.5 % | 4 of 5 | 355 | 40 | 37 | 111 | 0 |
| West North Central | Elevated | 15.4 % | 4 of 7 | 209 | 20 | 298 | 60 | 0 |
| South Atlantic | Elevated | 19.8 % | 7 of 9 | 374 | 38 | 502 | 359 | 2 |
| East South Central | Elevated | 15.1 % | 3 of 4 | 49 | 5 | 8 | 30 | 1 |
| West South Central | Elevated | 29.5 % | 1 of 4 | 300 | 23 | 2,037 | 776 | 2 |
| Mountain | Elevated | 12.3 % | 7 of 8 | 105 | 61 | 349 | 35 | 2 |
| Pacific | Normal | 7.2 % | 3 of 5 | 358 | 24 | 185 | 53 | 0 |
* Elevated means the % of visits for ILI is at or above the national or
region-specific baseline
† National data is for current week; regional data is for the most recent three weeks.
‡ Includes all 50 states and the District of Columbia
U.S. Virologic Surveillance:
WHO and NREVSS collaborating laboratories located in all 50 states and Washington D.C. report to CDC the number of respiratory specimens tested for influenza each week. The results of tests performed during the current week and cumulative totals for the season are summarized in the table below.
| Week 6 | Cumulative for the Season | |
|---|---|---|
| No. of specimens tested | 5,380 | 100,034 |
| No. of positive specimens (%) | 1,313 (24.4%) | 8,120 (8.1%) |
| Positive specimens by type/subtype | ||
| Influenza A | 904 (68.8%) | 6,442 (79.3%) |
| A (H1) | 272 (30.1%) | 2,120 (32.9%) |
| A (H3) | 12 (1.3%) | 249 (3.9%) |
| A (unsubtyped) | 620 (68.6%) | 4,037 (63.2%) |
| Influenza B | 409 (31.2%) | 1,678 (20.7%) |
Since week 1 (the week ending January 10, 2009), when influenza activity began to increase nationally, influenza A (H1) viruses have predominated circulation nationally each week and for the season overall in all regions. Since week 1, 90% of subtyped influenza A viruses reported to CDC were influenza A (H1).
View WHO-NREVSS Regional Bar Charts| View Chart Data | View Full Screen
Antigenic Characterization:
CDC has antigenically characterized 390 influenza viruses [239 influenza A (H1), 37 influenza A (H3) and 114 influenza B viruses] collected by U.S. laboratories since October 1, 2008.
All 239 influenza A (H1) viruses are related to the influenza A (H1N1) component of the 2008-09 influenza vaccine (A/Brisbane/59/2007). All 37 influenza A (H3N2) viruses are related to the A (H3N2) vaccine component (A/Brisbane/10/2007).
Influenza B viruses currently circulating can be divided into two distinct lineages represented by the B/Yamagata/16/88 and B/Victoria/02/87 viruses. Thirty-three influenza B viruses tested belong to the B/Yamagata lineage and are related to the vaccine strain (B/Florida/04/2006). The remaining 81 viruses belong to the B/Victoria lineage and are not related to the vaccine strain.
Data on antigenic characterization should be interpreted with caution given that antigenic characterization data is based on hemagglutination inhibition (HI) testing using a panel of reference ferret antisera and results may not correlate with clinical protection against circulating viruses provided by influenza vaccination.
Annual influenza vaccination is expected to provide the best protection against those virus strains that are related to the vaccine strains, but limited to no protection may be expected when the vaccine and circulating virus strains are so different as to be from different lineages, as is seen with the two lineages of influenza B viruses.
Antiviral Resistance:
Since October 1, 2008, 268 influenza A (H1N1), 51 influenza A (H3N2), and 110 influenza B viruses have been tested for resistance to the neuraminidase inhibitors (oseltamivir and zanamivir). Two hundred sixty-eight influenza A (H1N1) and 51 influenza A (H3N2) viruses have been tested for resistance to the adamantanes (amantadine and rimantadine). The results of antiviral resistance testing performed on these viruses are summarized in the table below.
| Isolates tested (n) | Resistant Viruses, Number (%) |
Isolates tested (n) | Resistant Viruses, Number (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oseltamivir | Zanamivir | Adamantanes | |||
| Influenza A (H1N1) | 268 | 264 (98.5%) | 0 (0) | 268 | 2 (0.7%) |
| Influenza A (H3N2) | 51 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 51 | 51 (100%) |
| Influenza B | 110 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | N/A* | N/A* |
Influenza A (H1N1) viruses from 33 states have been tested for antiviral resistance to oseltamivir so far this season. To date, all influenza A (H3N2) viruses tested are resistant to the adamantanes and all oseltamivir-resistant influenza A (H1N1) viruses tested are sensitive to the adamantanes. Influenza activity in the United States increased this week with influenza A (H1N1) viruses predominating overall. However, the level of activity and the relative proportion of circulating virus types or subtypes have varied by region and may vary over the course of the season. This presents challenges for the selection of antiviral medications for the treatment and chemoprophylaxis of influenza and highlights the importance of testing patients for influenza and consulting local surveillance data when evaluating patients with acute respiratory infections during the influenza season. CDC issued interim recommendations for the use of influenza antiviral medications in the setting of oseltamivir resistance among circulating influenza A (H1N1) viruses on December 19, 2008. These interim recommendations are available at http://www2a.cdc.gov/HAN/ArchiveSys/ViewMsgV.asp?AlertNum=00279
Pneumonia and Influenza (P&I) Mortality Surveillance
During week 6, 6.8% of all deaths reported through the 122-Cities Mortality Reporting System were due to P&I. This percentage is below the epidemic threshold of 8.0% for week 6.
View Full Screen
Influenza-Associated Pediatric Mortality
Six influenza-associated pediatric deaths were reported to CDC during week 6 (Arkansas, Colorado, Florida, North Carolina [2], and Pennsylvania). One death occurred during week 8 of the 2006-07 season (week ending February 24, 2007), bringing the total number of reported pediatric deaths occurring during that season to 78. The remaining five deaths reported this week occurred between January 25 and February 14, 2009. Since September 28, 2008, CDC has received nine reports of influenza-associated pediatric deaths that occurred during the current season.
Bacterial coinfections were confirmed in six (66.7%) of the nine children; Staphylococcus aureus was identified in four (66.7%) of the six children. Two of the S. aureus isolates were sensitive to methicillin and two were methicillin resistant. All six children with bacterial coinfections were five years of age or older. An increase in the number of influenza-associated pediatric deaths with bacterial coinfections was first recognized during the 2006-07 influenza season. In January 2008, interim testing and reporting recommendations were released regarding influenza and bacterial coinfections in children and are available at (http://www2a.cdc.gov/HAN/ArchiveSys/ViewMsgV.asp?AlertNum=00268).
View Full Screen
Influenza-Associated Hospitalizations
Laboratory-confirmed influenza-associated hospitalizations are monitored in two population-based surveillance networks: the Emerging Infections Program (EIP) and the New Vaccine Surveillance Network (NVSN).
No influenza-associated hospitalizations have been reported from the New Vaccine Surveillance Network this season.
During October 1, 2008 ?February 14, 2009, preliminary laboratory-confirmed influenza-associated hospitalization rates reported by the EIP for children aged 0-4 years and 5-17 years were 1.0 per 10,000 and 0.1 per 10,000, respectively. For adults aged 18-49 years, 50-64 years, and = 65 years, the rates were 0.1 per 10,000, 0.1 per 10,000, and 0.4 per 10,000, respectively.
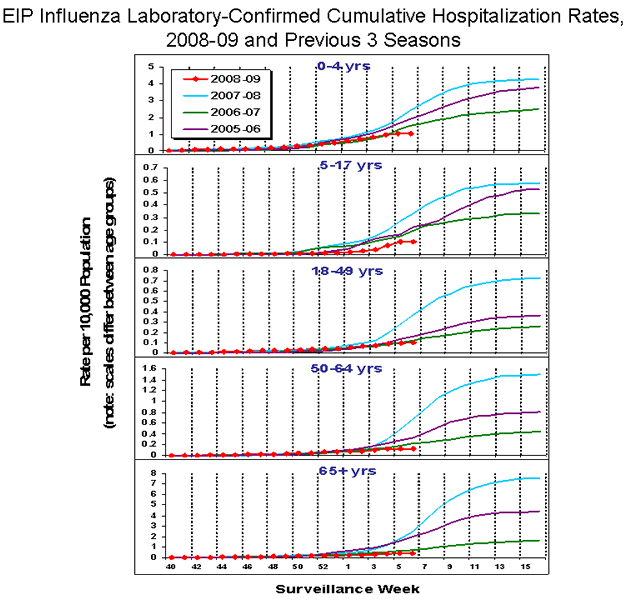
View Full Screen
Outpatient Illness Surveillance:
Nationwide during week 6, 3.6% of patient visits reported through the U.S. Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network (ILINet) were due to influenza-like illness (ILI). This percentage is above the national baseline of 2.4%.
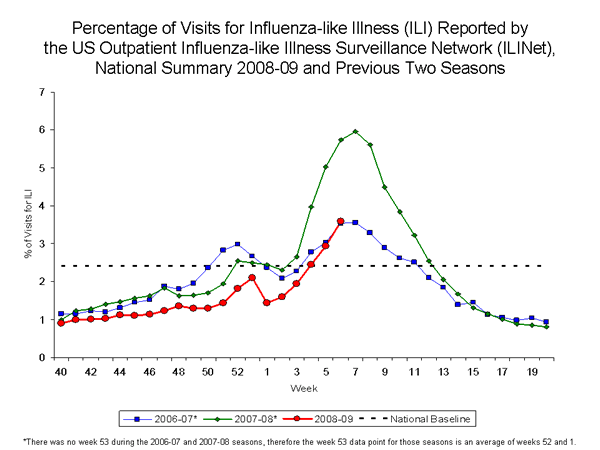
View Sentinel Providers Regional Charts | View Chart Data |View Full Screen
On a regional level, the percentage of visits for ILI increased in seven of the nine regions compared to the previous week and ranged from 1.7% to 6.6%. Eight of nine surveillance regions reported ILI percentages above their region specific baselines.
| Region | New England | Mid Atlantic | East North Central | West North Central | South Atlantic | East South Central | West South Central | Mountain | Pacific |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reported ILI (%) | 4.8 | 4.3 | 2.5 | 2.0 | 3.7 | 3.4 | 6.6 | 1.7 | 2.9 |
| Region-Specific Baseline | 1.5 | 2.9 | 1.9 | 1.7 | 2.2 | 2.5 | 4.8 | 1.5 | 3.0 |
Geographic Spread of Influenza as Assessed by State and Territorial Epidemiologists:
During week 6, the following influenza activity was reported:
- Widespread influenza activity was reported by 24 states (Alabama, Arizona, Colorado, Connecticut, Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Indiana, Iowa, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Nevada, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, North Carolina, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, South Carolina, Tennessee, Texas, and Virginia).
- Regional influenza activity was reported by 13 states (Alaska, California, Hawaii, Idaho, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, Montana, Nebraska, New Mexico, North Dakota, Wisconsin, and Wyoming).
- Local influenza activity was reported by the District of Columbia and 11 states (Arkansas, Kansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Missouri, Oklahoma, Oregon, South Dakota, Utah, Vermont, and Washington).
- Sporadic activity was reported by Puerto Rico and two states (Illinois and West Virginia).
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
A description of surveillance methods is available at: http://www.cy118119.com/flu/weekly/fluactivity.htm
- Page last updated February 13, 2009.