Persons using assistive technology might not be able to fully access information in this file. For assistance, please send e-mail to: mmwrq@cdc.gov. Type 508 Accommodation and the title of the report in the subject line of e-mail.
Obesity Prevalence Among Low-Income, Preschool-Aged Children --- United States, 1998--2008
Childhood obesity continues to be a leading public health concern that disproportionately affects low-income and minority children (1). Children who are obese in their preschool years are more likely to be obese in adolescence and adulthood (2) and to develop diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, asthma, and sleep apnea (3). One of the Healthy People 2010 objectives (19-3) is to reduce to 5% the proportion of children and adolescents who are obese (4). CDC's Pediatric Nutrition Surveillance System (PedNSS) is the only source of nationally compiled obesity surveillance data obtained at the state and local level for low-income, preschool-aged children participating in federally funded health and nutrition programs. To describe progress in reducing childhood obesity, CDC examined trends and current prevalence in obesity using PedNSS data submitted by participating states, territories, and Indian tribal organizations during 1998--2008. The findings indicated that obesity prevalence among low-income, preschool-aged children increased steadily from 12.4% in 1998 to 14.5% in 2003, but subsequently remained essentially the same, with a 14.6% prevalence in 2008. Reducing childhood obesity will require effective prevention strategies that focus on environments and policies promoting physical activity and a healthy diet for families, child care centers, and communities.
PedNSS is a state-based surveillance system that monitors the nutritional status of children from birth through age 4 years enrolled in federally funded programs that serve low-income children. For all states except California and North Carolina, data come exclusively from the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC).* In California, data are exclusively from Medicaid-funded programs. North Carolina submits data from both WIC (95.5%) and non-WIC programs (4.5%).? For the states included in this analysis, 21.0% of children aged 2--4 years are covered by PedNSS. On average, children are seen twice a year by the program; height and weight are measured each time. Data are collected at the clinic level and submitted to CDC for analysis. Federally funded programs submit data on weight, height (measured by trained staff using a standard protocol during clinic visits), age, sex, and the race/ethnicity reported by the child's parent or caregiver. CDC uses weight, height, and age data to calculate body mass index (BMI) (weight [kg] / height [m2]). For children aged 2--4 years, obesity is defined as BMI-for-age ≥95th percentile based on the 2000 CDC sex-specific growth charts (5). CDC performs routine edits to assess data quality. An error flag is applied to height or weight data that are either missing, miscoded, or biologically implausible (e.g., height-for-age z-score <-5.0 or >3.0, body mass index [BMI]-for-age [children aged ≥2 years] z-score <-4.0 or >5.0, weight-for-age z-score <-4.0 or >5.0, or BMI-for-age [children aged ≥2 years] z-score <-4.0 or >5.0). All flagged data are excluded from PedNSS analyses.
CDC randomly selected one record per child per year to estimate obesity prevalence in 1998, 2003, and 2008. To assess the change in obesity prevalence in PedNSS overall and by race/ethnicity, prevalence was estimated using data only from the subset of federally funded programs that participated in 1998, 2003, and 2008 (N = 37). The average annual change in obesity prevalence during 1998--2003 and 2003--2008 was estimated for each PedNSS program. If data for a program were unavailable for a given year but were available for the preceding or subsequent year, CDC substituted the data for the adjacent year and calculated the annual change to account for the shorter or longer period. Chi-square tests for difference in proportions were conducted across each period, and tests were statistically significant (p<0.05) unless otherwise noted in this report.
During 1998--2008, the number of federally funded programs reporting data to PedNSS varied from 43 to 52. In 2008, records on approximately 8 million children were submitted from 43 states, the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, the U.S. Virgin Islands, and six Indian tribal organizations (Table). The overall prevalence of obesity among low-income, preschool-aged children increased from 12.4% (n = 1,999,970) in 1998 to 14.5% (n = 1,967,625) in 2003 and 14.6% (n = 2,222,410) in 2008 (Figure). Obesity prevalence increased 0.43 percentage points annually during 1998--2003, but only 0.02 percentage points annually during 2003--2008. Obesity increased across all racial/ethnic groups during 1998--2003, with the exception of Asian/Pacific Islander (A/PI) children. However, during 2003--2008, obesity remained stable among all groups except American Indian/Alaska Native (AI/AN) children. In 2008, prevalence was highest among AI/AN (21.2%) and Hispanic (18.5%) children, and lowest among non-Hispanic white (12.6%), non-Hispanic black (11.8%), and A/PI (12.3%) children.
In 2008, only programs in Colorado and Hawaii had obesity prevalences ≤10%. The two federally funded programs with prevalence >20% were Indian tribal organizations (Table). Of the 41 PedNSS programs supplying data for 1998--2003, a total of 38 (93%) reported an increase in obesity prevalence. In contrast, of the 44 programs supplying data for 2003--2008, 22 (50%) reported an increase in obesity, whereas 14 (32%) reported no change, and eight (18%) reported a decrease.
Reported by: AJ Sharma, PhD, LM Grummer-Strawn, PhD, K Dalenius, MPH, D Galuska, PhD, M Anandappa, MS, E Borland, H Mackintosh, MSPH, R Smith, MS, Div of Nutrition, Physical Activity and Obesity, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, CDC.
Editorial Note:
Reduction of obesity among children and adolescents is a national priority in the United States (4). The results presented in this report indicate that among low-income, preschool-aged children participating in federally funded nutrition programs, the prevalence of obesity increased during 1998--2003, but stabilized during 2003--2008. In 2008, the national prevalence of obesity in this group remained highest among low-income Hispanic and AI/AN children and continued to increase among AI/AN children. These results suggest overall progress in stabilizing the prevalence of childhood obesity in a subset of low-income, preschool-aged children. However, these results should be confirmed through additional research using other data sets.
Children in preschool age groups are a priority for surveillance because obesity trends in this group can serve as a bellwether for trends in older children and adults (2). PedNSS currently serves as the only source of national obesity prevalence data compiled specifically on low-income, preschool-aged children. Because PedNSS nutritional data are dependent on enrollments in participating federally funded programs, PedNSS results are subject to variations in enrollment in these programs in each state. However, the effect of such variations on PedNSS results is difficult to determine. Conditions within a state that differentially affect the enrollment of children with varying prevalences of obesity could affect state or national results. In addition, changes in the proportion of children from each state might alter the results. For example, California, the largest data contributor to PedNSS, has one of the highest prevalences of obesity. The percentage of the total PedNSS sample provided by California decreased from 20.2% in 1998 to 13.6% in 2008. However, even deletion of all California data would not alter the overall results; an increase from 1998 to 2003 would still be observed, followed by stabilization through 2008. Furthermore, stabilization or declines were observed in half of the individual federally funded programs in PedNSS.
To maintain the consistency of PedNSS data, methods for data collection and recording are set nationally and are uniform across states and participating federal programs. The procedures for collecting height and weight data did not change during 1998--2008, with the exception of an increasing use of digital scales. Given the procedures within the WIC program for regular calibration of scales, this change should not affect rates of obesity. CDC has stringent requirements for data quality and uses standardized procedures for data cleaning; data files that do not meet these standards are rejected, as are records that do not meet standards for acceptable heights and weights.
The reason for the stabilization of overall obesity prevalence among these children during 2003--2008 is not known and likely is complex. One factor might be prevention efforts within state and local WIC programs targeting behaviors related to obesity in children. For example, certain initiatives in WIC§ have attempted to raise public awareness, acceptance, and support of breastfeeding, increased the percentage of low-fat or fat-free milk vouchers issued for children aged >2 years,? and reduced television viewing (6). Recommendations such as those from the Institute of Medicine's Preventing Childhood Obesity report also might have spurred greater attention to obesity prevention for all children (7).
The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) also has found a stabilization of obesity prevalence in U.S. children. NHANES found no significant increase in obesity prevalence during 1999--2006 in children aged 2--19 years (8). This apparent plateau remained even after adjusting for differences in prevalence by age group. Trends in the 2--5 year age group were not analyzed separately because of small sample size. For NHANES 2003--2006, the overall prevalence of obesity (BMI-for-age ≥95th percentile) for children aged 2--5 years was 12.4% (standard error = 1.0%), lower than the rates for both 2003 and 2008 described in this report.
The findings in this report are subject to at least three limitations. First, the proportion of children participating in federally funded nutrition programs increased during 1998--2008, as evidenced by the 11% increase in the number of children in these analyses (i.e., from 1,999,970 in 1998 to 2,222,410 in 2008). However, how the addition of these children might have affected the prevalence of obesity is unknown. Second, the percentage of the total PedNSS dataset that is made up of WIC records increased from 76% in 1998 to 85% in 2008. If the prevalence of obesity were lower in WIC than in non-WIC programs, this increase could partially explain the observed trends. However, when the analysis was conducted using only data from WIC, results were not substantially different. Finally, PedNSS data are not representative of all low-income, preschool-aged children in the United States because not all states participate in PedNSS and not all low-income children participate in federally funded programs.
Childhood obesity remains a serious public health problem even among this subset, particularly among AI/AN children. A sustained and effective public health response is necessary across the United States to reduce childhood obesity. Strategies should emphasize improving environments and policies that promote physical activity and a healthy diet.
References
- Wang Y, Beydoun MA. The obesity epidemic in the United States---gender, age, socioeconomic, racial/ethnic, and geographic characteristics: a systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Epidemiol Rev 2007;29:6--28.
- Serdula MK, Ivery D, Coates RJ, Freedman DS, Williamson DF, Byers T. Do obese children become obese adults? A review of the literature. Prev Med 1993;22:167--77.
- American Academy of Pediatrics. Policy statement: prevention of pediatric overweight and obesity. Pediatrics 2003;112:424--30.
- US Department of Health and Human Services. Healthy people 2010: objectives for improving health (part B: focus areas 15--28). 2nd ed. Washington, DC: US Department of Health and Human Services; 2000. Available at http://www.health.gov/healthypeople.
- Kuczmarski RJ, Ogden CL, Grummer-Strawn LM, et al. CDC growth charts: United States. Adv Data 2000;314:1--27. Available at http://www.cy118119.com/growthcharts.
- Johnson DB, Birkett D, Evens C, Pickering S. Statewide intervention to reduce television viewing in WIC clients and staff. Am J Health Promot 2005;19:418--21.
- Institute of Medicine. Preventing childhood obesity: health in the balance. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2005.
- Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Flegal KM. High body mass index for age among US children and adolescents, 2003--2006. JAMA 2008;299:2401--5.
* Eligibility criteria for WIC includes a family income ≤185% of the poverty income threshold, based on U.S. Poverty Income Guidelines, available at http://aspe.os.dhhs.gov/poverty. A person who participates or has family members who participate in certain other benefit programs, such as the Medicaid or Aid to Families with Dependent Children/Temporary Assistance to Needy Families, automatically meets the income-eligibility requirement.
? Including the Early and Periodic Screening, Diagnosis, and Treatment Program, other Medicaid-funded child health programs, and Title V Maternal and Child Health Programs. Eligibility criteria includes a family income ≤200% of the poverty income threshold, based on U.S. Poverty Income Guidelines. The non-WIC records accounted for 24% of records in 1998, 19% in 2003, and 15% in 2008.
§ Additional information available at http://www.nal.usda.gov/wicworks/spotlight/bfweek_resources.html.
? Additional information available at http://www.health.state.ny.us/prevention/nutrition/resources/docs/2003-2006_ewph_community_intervention_projects.pdf.
|
TABLE. Average annual change in obesity* prevalence among children aged 2--4 years, by state, territory, and Indian tribal organization? --- Pediatric Nutrition Surveillance System, United States, 1998--2003 and 2003--2008 |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
State, territory, or Indian tribal organization |
Average percentage-point change per year |
|||||||
|
1998 |
2003 |
2008 |
||||||
|
No. of children |
Obesity prevalence (%) |
No. of children |
Obesity prevalence (%) |
No. of children |
Obesity prevalence (%) |
1998--2003 |
2003--2008 |
|
|
Alabama |
39,998 |
11.7 |
30,221 |
14.7? |
56,813 |
13.8 |
0.50 |
-0.23 |
|
Arizona |
51,279 |
9.7 |
67,618 |
12.4? |
75,338 |
14.6 |
0.45 |
0.55 |
|
Arkansas |
34,968 |
9.7 |
31,625 |
12.2 |
38,591 |
13.9 |
0.50 |
0.34 |
|
California |
398,222 |
15.5 |
344,384 |
17.6 |
301,643 |
17.3 |
0.42 |
-0.06 |
|
Colorado |
---§ |
--- |
50,773 |
9.4 |
43,476 |
9.4 |
--- |
0.00** |
|
Connecticut |
23,272 |
17.8 |
22,495 |
19.6 |
25,623 |
15.5 |
0.36 |
-0.82 |
|
Florida |
141,831 |
11.3 |
155,482 |
13.4 |
209,671 |
14.1 |
0.42 |
0.14 |
|
Georgia |
87,823 |
9.4 |
92,728 |
12.4 |
124,533 |
14.8 |
0.60 |
0.48 |
|
Hawaii |
3,649 |
10.3 |
15,602 |
10.1 |
16,106 |
9.3 |
-0.04** |
-0.16 |
|
Idaho |
15,121 |
9.8 |
16,340 |
11.2 |
20,081 |
12.3 |
0.28 |
0.22 |
|
Illinois |
88,178 |
13.5 |
70,666 |
13.9 |
63,414 |
14.7 |
0.08 |
0.16 |
|
Indiana |
64,411 |
10.5 |
51,953 |
13.7 |
66,499 |
14.5 |
0.64 |
0.16 |
|
Iowa |
29,788 |
10.6 |
32,913 |
13.9 |
33,548 |
15.1 |
0.66 |
0.24 |
|
Kansas |
22,628 |
8.8 |
27,076 |
12.6 |
34,352 |
13.3 |
0.76 |
0.14 |
|
Kentucky |
48,075 |
12.1 |
60,984 |
17.2 |
62,832 |
15.7 |
1.02 |
-0.30 |
|
Louisiana |
45,834 |
10.4 |
44,036 |
13.3 |
34,041 |
13.8? |
0.58 |
0.13 |
|
Maine |
11,747 |
12.1 |
9,861 |
15.8 |
--- |
--- |
0.74 |
--- |
|
Maryland |
23,329 |
12.0 |
42,884 |
14.4? |
54,866 |
15.7 |
0.40 |
0.33 |
|
Massachusetts |
59,511 |
14.8 |
55,785 |
16.7 |
59,297 |
16.7 |
0.38 |
0.00** |
|
Michigan |
90,760 |
10.1 |
93,962 |
12.9 |
103,523 |
13.9 |
0.56 |
0.20 |
|
Minnesota |
76,271 |
11.0 |
40,161 |
13.2 |
65,607 |
13.4 |
0.44 |
0.04** |
|
Mississippi |
11,850 |
13.2 |
--- |
--- |
44,807 |
14.6 |
--- |
--- |
|
Missouri |
58,000 |
9.8 |
56,346 |
13.3 |
60,908 |
13.9 |
0.70 |
0.12 |
|
Montana |
9,658 |
9.0 |
10,178 |
11.0 |
10,428 |
12.4 |
0.40 |
0.28 |
|
Nebraska |
13,961 |
9.9 |
17,242 |
13.4 |
20,658 |
13.9 |
0.70 |
0.10** |
|
Nevada |
6,123 |
11.6 |
14,595 |
13.6 |
23,348 |
12.9 |
0.40 |
-0.14 |
|
New Hampshire |
5,530 |
13.5 |
7,227 |
15.6 |
8,082 |
15.5 |
0.42 |
-0.02** |
|
New Jersey |
56,292 |
15.1 |
56,774 |
17.9 |
68,163 |
17.9 |
0.56 |
0.00** |
|
New Mexico |
17,523 |
7.6 |
27,555 |
9.7 |
22,295 |
12.0 |
0.42 |
0.46 |
|
New York |
207,479 |
14.7 |
186,284 |
16.6 |
209,713 |
14.6 |
0.38 |
-0.40 |
|
North Carolina |
80,956 |
11.1 |
75,206 |
14.5 |
96,381 |
15.7 |
0.68 |
0.24 |
|
North Dakota |
7,246 |
9.4 |
6,097 |
11.6 |
6,551 |
13.8 |
0.44 |
0.44 |
|
Ohio |
17,219 |
10.4 |
89,824 |
11.6 |
125,011 |
12.2 |
0.24 |
0.12 |
|
Oregon |
34,546 |
11.9 |
29,875 |
14.7 |
49,193 |
14.7 |
0.56 |
0.00** |
|
Pennsylvania |
108,858 |
10.7 |
100,053 |
12.4 |
111,879 |
11.5 |
0.34 |
-0.18 |
|
Rhode Island |
--- |
--- |
--- |
--- |
11,466 |
16.2 |
--- |
--- |
|
South Carolina |
48,543 |
10.0 |
32,239 |
12.4 |
28,209 |
13.3 |
0.48 |
0.18 |
|
South Dakota |
8,968 |
9.0 |
8,423 |
13.6 |
9,125 |
16.2 |
0.92 |
0.52 |
|
Tennessee |
56,208 |
10.0 |
60,086 |
12.0 |
49,016 |
13.8 |
0.40 |
0.36 |
|
Texas |
--- |
--- |
422,127 |
14.4 |
164,435 |
16.2 |
--- |
0.36 |
|
Utah |
23,765 |
6.5 |
31,099 |
8.6 |
--- |
--- |
0.42 |
--- |
|
Vermont |
6,225 |
11.6 |
8,504 |
13.1 |
7,009 |
13.3 |
0.30 |
0.04** |
|
Virginia |
--- |
--- |
20,238 |
18.5 |
59,627 |
19.0 |
--- |
0.10** |
|
Washington |
55,162 |
12.0 |
65,828 |
13.8? |
92,980 |
14.4 |
0.45 |
0.10 |
|
West Virginia |
24,170 |
10.6 |
22,079 |
13.2 |
22,689 |
13.5 |
0.52 |
0.06** |
|
Wisconsin |
52,186 |
10.1 |
50,284 |
13.0 |
55,875 |
13.6 |
0.58 |
0.12 |
|
Wyoming |
--- |
--- |
5,269 |
9.5 |
--- |
--- |
--- |
--- |
|
District of Columbia |
6,499 |
10.9 |
5,926 |
13.3 |
6,195 |
13.3 |
0.48 |
0.00** |
|
Puerto Rico |
--- |
--- |
102,624 |
24.0 |
99,829 |
17.9 |
--- |
-1.22 |
|
U.S. Virgin Islands |
--- |
--- |
--- |
--- |
2,339 |
13.6 |
--- |
--- |
|
Cheyenne River Sioux Tribe (SD) |
362 |
22.1? |
388 |
17.5 |
423 |
18.4 |
-1.15** |
0.18** |
|
Chickasaw Nation (OK) |
1,039 |
8.9 |
1,478 |
12.0 |
--- |
--- |
0.62 |
--- |
|
Inter Tribal Council of Arizona |
4,680 |
19.8 |
5,037 |
20.9 |
5,823 |
23.5 |
0.22** |
0.52 |
|
Navajo Nation |
--- |
--- |
7,616 |
14.4 |
6,824 |
16.9 |
--- |
0.50 |
|
Rosebud Sioux Tribe (SD) |
604 |
16.4 |
641 |
17.3 |
651 |
19.2 |
0.18** |
0.38** |
|
Standing Rock Sioux Tribe (ND) |
--- |
--- |
422 |
20.1 |
541 |
25.0 |
--- |
0.98** |
|
Three Affiliated Tribes (ND) |
--- |
--- |
--- |
--- |
163 |
19.6 |
--- |
--- |
|
* Defined as body mass index (BMI)-for-age ≥95th percentile based on the 2000 CDC sex-specific growth charts, available at http://www.cy118119.com/growthcharts. ? Data from subsequent year used. § Data not available. ? Data from preceding year used. ** No significant change in obesity prevalence. |
||||||||
FIGURE. Change in obesity* prevalence during 1998--2003 and 2003--2008 among children aged 2--4 years, by race/ethnicity --- Pediatric Nutrition Surveillance System, United States, 1998--2008?
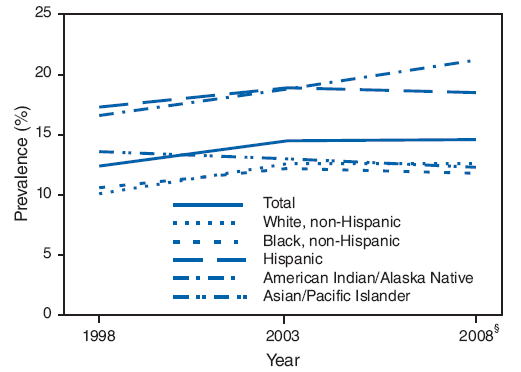
* Defined as body mass index (BMI)-for-age ≥95th percentile based on the 2000 CDC sex-specific growth charts, available at http://www.cy118119.com/growthcharts.
? Includes only the 37 federally funded programs that provided data in 1998, 2003, and 2008.
§ Sample sizes in 2008 were as follows: total, 2,222,410; non-Hispanic white, 845,910; non-Hispanic black, 438,645; Hispanic, 749,109; American Indian/Alaska Native, 23,960; and Asian/Pacific Islander, 68,933.
Alternative Text: The figure above shows changes in obesity prevalence from the period 1998-2003 to the period 2003-2008 among U.S. children aged 2-4 years, by race/ethnicity, based on date from the Pediatric Nutrition Surveillance System. Overall, obesity prevalence among these low-income, preschool-aged children enrolled in federally funded nutrition programs increased steadily from 12.4% in 1998 to 14.5% in 2003, but subsequently remained essentially the same, with a 14.6% prevalence in 2008. Obesity increased across all racial/ethnic groups during 1998-2003, with the exception of Asian/Pacific Islander children. However, during 2003-2008, obesity remained stable among all groups except American Indian/Alaska Native children. In 2008, prevalence was highest among American Indian/Alaska Native (21.2%) and Hispanic (18.5%) children, and lowest among non-Hispanic white (12.6%), non-Hispanic black (11.8%), and Asian/Pacific Islander (12.3%) children.
Use of trade names and commercial sources is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by the U.S. Department of
Health and Human Services. |
All MMWR HTML versions of articles are electronic conversions from typeset documents. This conversion might result in character translation or format errors in the HTML version. Users are referred to the electronic PDF version (http://www.cy118119.com/mmwr) and/or the original MMWR paper copy for printable versions of official text, figures, and tables. An original paper copy of this issue can be obtained from the Superintendent of Documents, U.S. Government Printing Office (GPO), Washington, DC 20402-9371; telephone: (202) 512-1800. Contact GPO for current prices.
**Questions or messages regarding errors in formatting should be addressed to mmwrq@cdc.gov.Date last reviewed: 7/23/2009


