Error processing SSI file

2012-2013 Influenza Season Week 41 ending October 13, 2012
All data are preliminary and may change as more reports are received.
Synopsis:
During week 41 (October 7-13, 2012), influenza activity remained low in the United States.
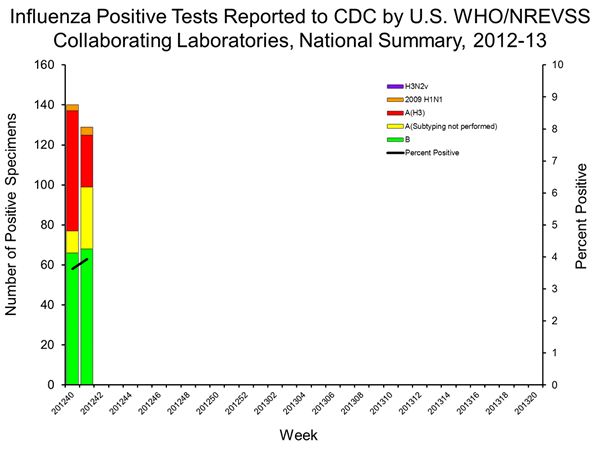
- Viral Surveillance: Of 3,285 specimens tested and reported by U.S. World Health Organization (WHO) and National Respiratory and Enteric Virus Surveillance System (NREVSS) collaborating laboratories during week 41, 129 (3.9%) were positive for influenza.
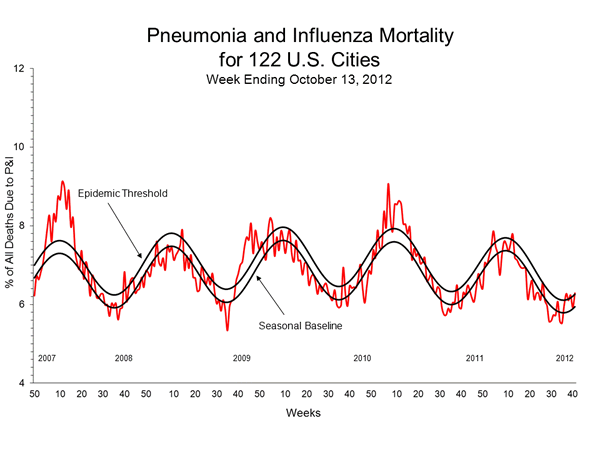
- Pneumonia and Influenza Mortality: The proportion of deaths attributed to pneumonia and influenza (P&I) was at the epidemic threshold.
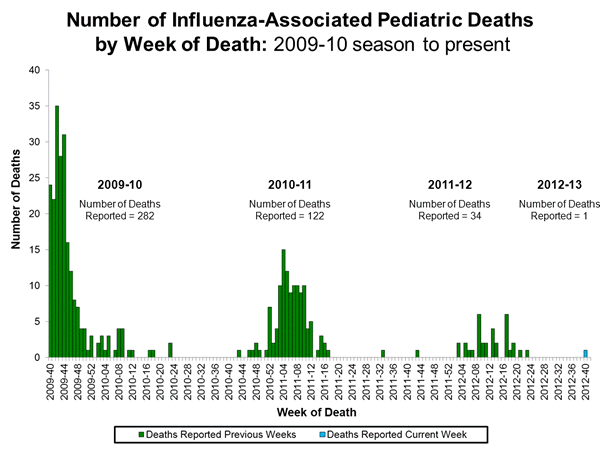
- Influenza-associated Pediatric Deaths: One influenza-associated pediatric death was reported and was associated with an influenza A virus for which the subtype was not determined.
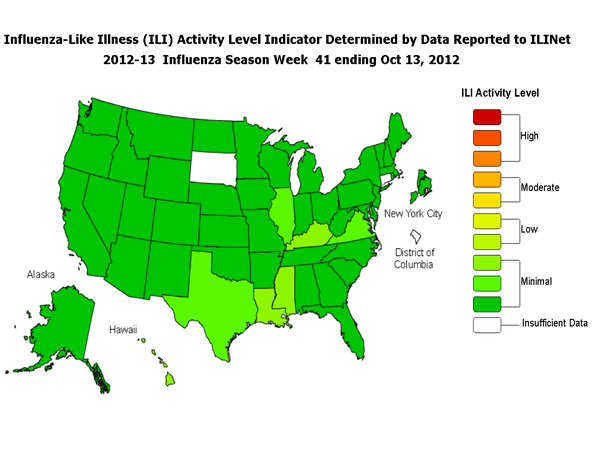
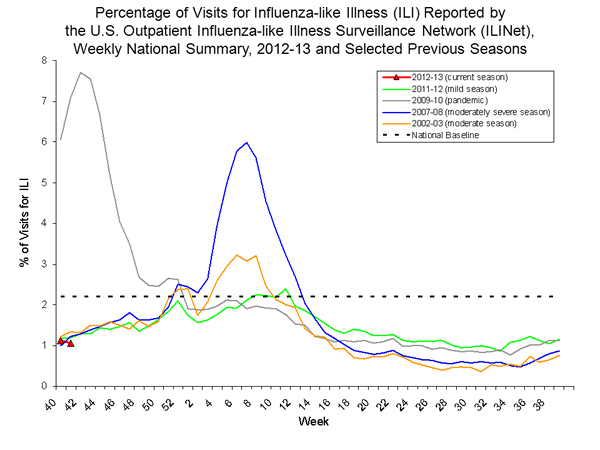
- Outpatient Illness Surveillance: The proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) was 1.1%, which is below the national baseline of 2.2%. All 10 regions reported ILI below region-specific baseline levels. Forty-eight states and New York City experienced minimal ILI activity and the District of Columbia and two states had insufficient data.
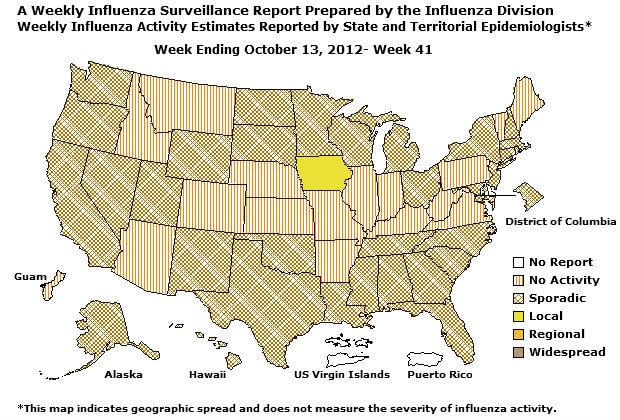
- Geographic Spread of Influenza: The geographic spread of influenza in one state (Iowa) was reported as local; the District of Columbia and 32 states reported sporadic activity; Guam and 16 states reported no influenza activity, and Puerto Rico, the U.S. Virgin Islands, and one state did not report.
| HHS Surveillance Regions* | Data for current week | Data cumulative since September 30, 2012 (Week 40) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Out-patient ILI† | % positive for flu‡ | Number of jurisdictions reporting regional or widespread activity§ | 2009 H1N1 | A (H3) | A(Subtyping not performed) | B | Pediatric Deaths | |||
| Nation | Normal | 3.9% | 0 of 54 | 7 | 86 | 42 | 134 | 1 | ||
| Region 1 | Normal | 0.4% | 0 of 6 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Region 2 | Normal | 0.9% | 0 of 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 0 | ||
| Region 3 | Normal | 1.0% | 0 of 6 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Region 4 | Normal | 7.7% | 0 of 8 | 3 | 15 | 30 | 82 | 1 | ||
| Region 5 | Normal | 3.9% | 0 of 6 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 9 | 0 | ||
| Region 6 | Normal | 2.6% | 0 of 5 | 0 | 6 | 2 | 20 | 0 | ||
| Region 7 | Normal | 3.9% | 0 of 4 | 0 | 11 | 6 | 14 | 0 | ||
| Region 8 | Normal | 2.1% | 0 of 6 | 0 | 16 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Region 9 | Normal | 2.5% | 0 of 5 | 0 | 10 | 3 | 3 | 0 | ||
| Region 10 | Normal | 3.9% | 0 of 4 | 0 | 20 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
*HHS regions (Region 1 CT, ME, MA, NH, RI, VT; Region 2: NJ, NY, Puerto Rico, US Virgin Islands; Region 3: DE, DC, MD, PA, VA, WV; Region 4: AL, FL, GA, KY, MS, NC, SC, TN; Region 5: IL, IN, MI, MN, OH, WI; Region 6: AR, LA, NM, OK, TX; Region 7: IA, KS, MO, NE; Region 8: CO, MT, ND, SD, UT, WY; Region 9: AZ, CA, Guam, HI, NV; and Region 10: AK, ID, OR, WA).
† Elevated means the % of visits for ILI is at or above the national or region-specific baseline
‡ National data are for current week; regional data are for the most recent three weeks
§ Includes all 50 states, the District of Columbia, Guam, Puerto Rico, and U.S. Virgin Islands
U.S. Virologic Surveillance:
WHO and NREVSS collaborating laboratories located in all 50 states and Washington, D.C. report to CDC the number of respiratory specimens tested for influenza and the number positive by influenza type and subtype. Region specific data can be found at http://gis.cdc.gov/grasp/fluview/fluportaldashboard.html.
| Week 41 | |
|---|---|
| No. of specimens tested | 3,285 |
| No. of positive specimens (%) | 129 (3.9%) |
| Positive specimens by type/subtype | |
| Influenza A | 61 (47%) |
| 2009 H1N1 | 4 (6.6%) |
| Subtyping not performed | 31 (50.8%) |
| H3 | 26 (42.6%) |
| Influenza B | 68 (53%) |
View National and Regional Level Graphs and Data | View Chart Data | View Full Screen | View PowerPoint Presentation
Novel Influenza A Virus:
No new variant influenza virus infections have been reported since last week’s update. A total of 310 infections with variant influenza viruses (306 H3N2v viruses, 3 H1N2v viruses, and one H1N1v virus) have been reported from ten states since July 12. The vast majority of cases have occurred after prolonged swine exposure, though instances of likely human-to-human transmission have been identified. At this time no ongoing human-to-human transmission has been identified.
Additional information on influenza in swine, variant influenza infection in humans, and strategies to interact safely with swine can be found at http://www.cy118119.com/flu/swineflu/h3n2v-outbreak.htm.
Antigenic Characterization:
No antigenic characterization data is available for specimens collected after October 1, 2012.
Antiviral Resistance:
No antiviral resistance data is available for specimens collected after October 1, 2012. Of specimens collected between May and September 2012 and tested for susceptibility to the neuraminidase inhibitors (oseltamivir and zanamivir), only one virus, a 2009 H1N1 virus, was found to be resistant to oseltamivir. This virus was sensitive to zanamivir.
High levels of resistance to the adamantanes (amantadine and rimantadine) persist among 2009 H1N1 and A (H3N2) viruses (the adamantanes do not have activity against influenza B viruses). Antiviral treatment as early as possible with oseltamivir or zanamivir is recommended for patients with confirmed or suspected influenza who have severe, complicated, or progressive illness; who require hospitalization; or who are at greater risk for influenza-related complications. Additional information treatment and chemoprophylaxis of influenza virus infection with antiviral agents is available at http://www.cy118119.com/flu/antivirals/index.htm.Pneumonia and Influenza (P&I) Mortality Surveillance:
During week 41, 6.3% of all deaths reported through the 122-Cities Mortality Reporting System were due to P&I. This percentage was at the epidemic threshold of 6.3% for week 41.
View Full Screen | View PowerPoint Presentation
Influenza-Associated Pediatric Mortality:
One influenza-associated pediatric death was reported to CDC during week 41 and was associated with an influenza A virus for which the subtype was not determined. The death reported during week 41 occurred during the week ending October 6, 2012 (week 40). Additional data can be found at: http://gis.cdc.gov/GRASP/Fluview/PedFluDeath.html.
Influenza-Associated Hospitalizations:
The Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network (FluSurv-NET) conducts all age population-based surveillance for laboratory-confirmed influenza-related hospitalizations in select counties in the Emerging Infections Program (EIP) states and Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Project (IHSP) states. FluSurv-NET estimated hospitalization rates will be updated weekly starting later this season. Additional FluSurv-NET data can be found at: http://gis.cdc.gov/GRASP/Fluview/FluHospRates.html.
Outpatient Illness Surveillance:
Nationwide during week 41, 1.1% of patient visits reported through the U.S. Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network (ILINet) were due to influenza-like illness (ILI). This percentage is below the national baseline of 2.2%. (ILI is defined as fever (temperature of 100°F [37.8°C] or greater) and cough and/or sore throat.) Region specific data is available at http://gis.cdc.gov/grasp/fluview/fluportaldashboard.html.
View National and Regional Level Graphs and Data | View Chart Data | View Full Screen | View PowerPoint Presentation
On a regional level, the percentage of outpatient visits for ILI ranged from 0.4% to 2.0% during week 41. All 10 regions reported a proportion of outpatient visits for ILI below their region-specific baseline levels.
ILINet State Activity Indicator Map:
Data collected in ILINet are used to produce a measure of ILI activity* by state. Activity levels are based on the percent of outpatient visits in a state due to ILI and are compared to the average percent of ILI visits that occur during spring and fall weeks with little or no influenza virus circulation. Activity levels range from minimal, which would correspond to ILI activity from outpatient clinics being below the average, to intense, which would correspond to ILI activity from outpatient clinics being much higher than average.
During week 41, the following ILI activity levels were experienced:
- Forty-eight states and New York City experienced minimal ILI activity (Alabama, Alaska, Arizona, Arkansas, California, Colorado, Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Hawaii, Idaho, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Montana, Nebraska, Nevada, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New Mexico, New York, North Carolina, North Dakota, Ohio, Oklahoma, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, South Carolina, Tennessee, Texas, Utah, Vermont, Virginia, Washington, West Virginia, Wisconsin, and Wyoming).
- Data were insufficient to calculate an ILI activity level from the District of Columbia and two states (Connecticut and South Dakota).
*This map uses the proportion of outpatient visits to health care providers for influenza-like illness to measure the ILI activity level within a state. It does not, however, measure the extent of geographic spread of flu within a state. Therefore, outbreaks occurring in a single city could cause the state to display high activity levels.
Data collected in ILINet may disproportionately represent certain populations within a state, and therefore, may not accurately depict the full picture of influenza activity for the whole state.
Data displayed in this map are based on data collected in ILINet, whereas the State and Territorial flu activity map are based on reports from state and territorial epidemiologists. The data presented in this map is preliminary and may change as more data is received.
Differences in the data presented here by CDC and independently by some state health departments likely represent differing levels of data completeness with data presented by the state likely being the more complete.
Geographic Spread of Influenza as Assessed by State and Territorial Epidemiologists:
The influenza activity reported by state and territorial epidemiologists indicates geographic spread of influenza viruses, but does not measure the intensity of influenza activity.
During week 41, the following influenza activity was reported:
- Local influenza activity was reported by one state (Iowa).
- Sporadic influenza activity was reported by the District of Columbia and 32 states (Alabama, Alaska, California, Connecticut, Florida, Georgia, Hawaii, Louisiana, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, Nevada, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New Mexico, New York, North Carolina, North Dakota, Ohio, Oklahoma, Oregon, Rhode Island, South Carolina, South Dakota, Tennessee, Texas, Utah, Washington, Wisconsin, and Wyoming).
- No influenza activity was reported by Guam and 16 states (Arizona, Arkansas, Colorado, Idaho, Illinois, Indiana, Kansas, Kentucky, Maine, Missouri, Montana, Nebraska, Pennsylvania, Vermont, Virginia, and West Virginia).
- Puerto Rico, the U.S. Virgin Islands, and one state (Delaware) did not report.
- Content Source: Coordinating Center for Infectious Diseases (CCID)
- National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases (NCIRD)
Flu Activity data in XML Format | View Full Screen
Additional National and International Influenza Surveillance Information
FluView Interactive: This season, FluView includes enhanced web-based interactive applications which can provide dynamic visuals of the influenza data collected and analyzed by CDC. These FluView Interactive applications, allow people to create customized, visual interpretations of influenza data, as well as comparisons across flu seasons, regions, age groups, and a variety of other demographics. To access these tools visit http://www.cy118119.com/flu/weekly/fluviewinteractive.htm.
U.S. State and local influenza surveillance: Click on a jurisdiction below to access the latest local influenza information.
Google Flu Trends: Google Flu Trends uses aggregated Google search data in a model created in collaboration with CDC to estimate influenza activity in the United States. For more information and activity estimates from the U.S. and worldwide, see http://www.google.org/flutrends/
Europe: for the most recent influenza surveillance information from Europe, please see WHO/Europe at http://www.euroflu.org/index.php and visit the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control at http://ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications/surveillance_reports/influenza/Pages/weekly_influenza_surveillance_overview.aspx
Public Health Agency of Canada: The most up-to-date influenza information from Canada is available at http://www.phac-aspc.gc.ca/fluwatch/
World Health Organization FluNet: Additional influenza surveillance information from participating WHO member nations is available at FluNet and the Global Epidemiology Reports
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
A description of surveillance methods is available at: http://www.cy118119.com/flu/weekly/overview.htm