Error processing SSI file
Error processing SSI file
Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update
Week ending December 3, 2005-Week 48
Error processing SSI fileSynopsis:
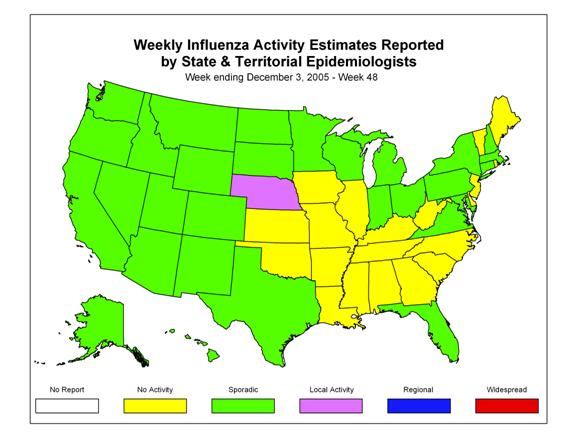
During week 48 (November 27 ?December 3, 2005)*, influenza activity occurred at a low level in the United States. Twenty-four (1.3%) specimens tested by U.S. World Health Organization (WHO) and National Respiratory and Enteric Virus Surveillance System (NREVSS) collaborating laboratories were positive for influenza. The proportion of patient visits to sentinel providers for influenza-like illness (ILI) and the proportion of deaths attributed to pneumonia and influenza were below baseline levels. One state reported local influenza activity; 29 states, New York City, and Puerto Rico reported sporadic influenza activity; and 20 states and the District of Columbia reported no influenza activity.
Laboratory Surveillance*:
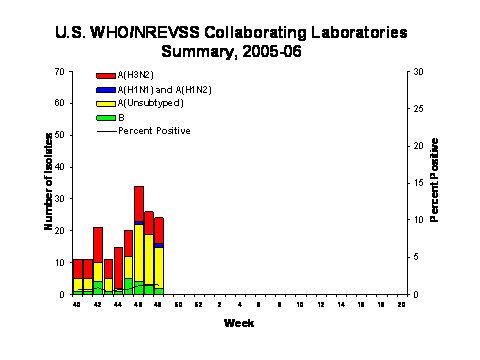
During week 48, WHO and NREVSS laboratories reported 1,897 specimens tested for influenza viruses and 24 (1.3%) were positive. Of these, 8 were influenza A (H3N2) viruses, 1 was an influenza A (H1N1) virus, 13 were influenza A viruses that were not subtyped, and 2 were influenza B viruses.
Since October 2, WHO and NREVSS laboratories have tested a total of 20,336 specimens for influenza viruses and 173 (0.9%) were positive. Among the 173 influenza viruses, 151 (87.3%) were influenza A viruses and 22 (12.7%) were influenza B viruses. Seventy-eight (51.7%) of the 151 influenza A viruses have been subtyped; 76 (97.4%) were influenza A (H3N2) viruses and 2 (2.6%) were influenza A (H1N1) viruses. Thirty states from all surveillance regions** have reported laboratory-confirmed influenza this season. Sixty-four (37.0%) of the 173 isolates have been reported by the Pacific region and 45 (26.0%) were from the Mountain region.
Antigenic Characterization:
CDC has antigenically characterized 16 influenza viruses collected by U.S. laboratories since October 1, 2005: 14 influenza A (H3N2) virus and 2 influenza B viruses. The influenza A (H3N2) viruses were characterized as A/California/07/2004-like, which is the influenza A (H3N2) component recommended for the 2005-06 influenza vaccine. Influenza B viruses currently circulating can be divided into two antigenically distinct lineages represented by B/Yamagata/16/88 and B/Victoria/2/87 viruses. One of the influenza B viruses isolated belonged to the B/Yamagata lineage and was characterized as B/Florida/07/2004-like. This is a minor antigenic variant of B/Shanghai/361/2002, the recommended influenza B component for the 2005-06 influenza vaccine. The other influenza B virus was identified as belonging to the B/Victoria lineage.
Pneumonia and Influenza (P&I) Mortality Surveillance*:
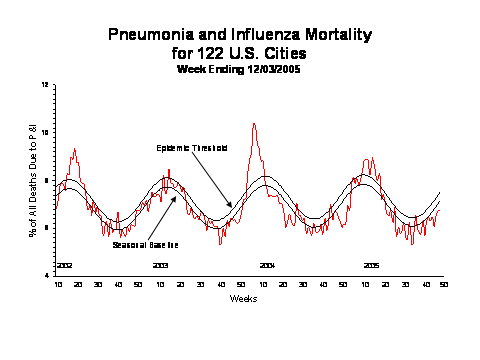
During week 48, 6.7% of all deaths reported by the vital statistics offices of 122 U.S. cities were reported as due to pneumonia or influenza. This percentage is below the epidemic threshold of 7.5% for week 48.
Influenza-Associated Pediatric Mortality*:
One influenza-associated pediatric death was reported for week 48. Since October 2, 2005, CDC has received reports of two influenza-associated pediatric deaths, one of which occurred during the 2004-05 influenza season.
Influenza-Associated Pediatric Hospitalizations*:
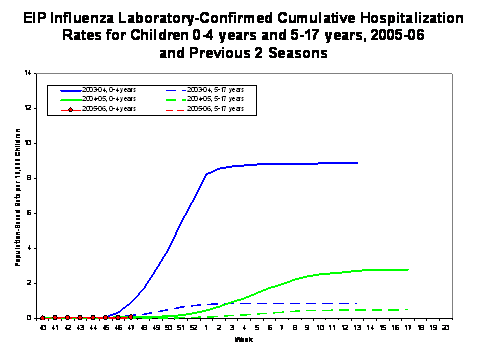
Laboratory-confirmed influenza-associated pediatric hospitalizations are monitored in two population-based surveillance networks?/sup>: the Emerging Infections Program (EIP) and the New Vaccine Surveillance Network (NVSN). During October 1 ?November 26, 2005, the preliminary influenza-associated hospitalization rate for children 0? years old reported by the EIP was 0.06 per 10,000. The EIP also monitors hospitalizations in children 5-17 years old. There were no influenza-associated hospitalizations for this age group reported during this period. The overall hospitalization rate reported by the EIP for children aged 0-17 years was 0.02 per 10,000. During October 30 ?November 26, 2005, there were no laboratory-confirmed influenza-associated hospitalizations for children 0 ?4 years old in the NVSN. EIP and NVSN hospitalization rate estimates are preliminary and may change as data continue to be collected.
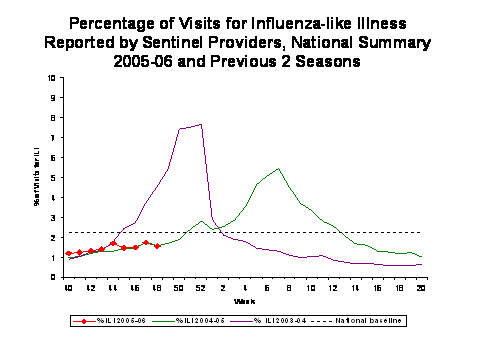
Influenza-like Illness Surveillance*:
During week 48, 1.6%*** of patient visits to U.S. sentinel providers were due to ILI. This percentage is less than the national baseline of 2.2%. On a regional level**, the percentage of visits for ILI ranged from 0.2% to 2.6%. Due to wide variability in regional level data, it is not appropriate to apply the national baseline to regional level data.
View
Chart Data
| View Full Screen
Influenza Activity as Assessed by State and Territorial Epidemiologists*:
During week 48, Nebraska reported local influenza activity. Twenty-nine states (Alaska, Arizona, California, Colorado, Connecticut, Florida, Hawaii, Idaho, Indiana, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Montana, Nevada, New Hampshire, New Mexico, New York, North Dakota, Ohio, Oregon, Pennsylvania, South Dakota, Texas, Utah, Virginia, Washington, Wisconsin, and Wyoming), New York City, and Puerto Rico reported sporadic influenza activity. Twenty states and the District of Columbia reported no influenza activity.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Report prepared: December 9, 2005
Error processing SSI file